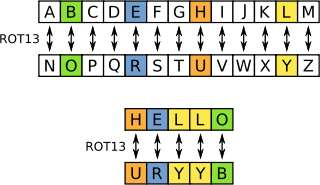
"ROT13 ("rotate by 13 places", sometimes hyphenated ROT-13) is a simple letter substitution cipher that replaces a letter with the letter 13 letters after it in the alphabet. ROT13 is a special case of the Caesar cipher, developed in ancient Rome." -- Wikipedia
import string
def rot13(text):
if isinstance(text, str):
rot13 = string.maketrans("ABCDEFGHIJKLMabcdefghijklmNOPQRSTUVWXYZnopqrstuvwxyz",
"NOPQRSTUVWXYZnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMabcdefghijklm")
return string.translate(text, rot13)
else:
raise ValueError("The parameter must be a string.")
2. Second Approach
But the problem with the above solution is that maketrans was removed in Python3. Instead we can use bytes.maketrans() for the purpose, so in order to obtain a more generalised solution we can do it as follows :-
import string
import sys
def rot13(text):
if isinstance(text, str):
if sys.version[0] == "2":
rot13_data = string.maketrans("ABCDEFGHIJKLMabcdefghijklmNOPQRSTUVWXYZnopqrstuvwxyz",
"NOPQRSTUVWXYZnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMabcdefghijklm")
return string.translate(text, rot13_data)
elif sys.version[0] == "3":
rot13_data = bytes.maketrans(b"ABCDEFGHIJKLMabcdefghijklmNOPQRSTUVWXYZnopqrstuvwxyz",
b"NOPQRSTUVWXYZnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMabcdefghijklm")
return text.translate(rot13_data)
else:
raise ValueError("The parameter must be a string.")
You can simple send your rot13 cipher/plaintext and it will encode or decode accordingly.
3. Third Approach
Another better technique is to use codecs module and use the in built rot_13 encoding scheme which is the same. Also its more preferable.
import codecs
cipher = codecs.encode("Natsu Dragneel", "rot_13")
print(cipher)
plain = codecs.decode(cipher, "rot_13")
print(plain)

















